Glycerol monostearatehow to dissolve glycerol monostearate, glycerol monostearate banned, glycerol monostearate vegan, glycerol monostearate solubility, glycerol monostearate e471, glycerol monostearate safety, glycerol monostearate in cosmetics, glycerol monostearate halal
Glycerol monostearate
Glycerol monostearate, commonly known as GMS, is a monoglyceride commonly used as an emulsifier in foods.[3] It takes the form of a white, odorless, and sweet-tasting flaky powder that is hygroscopic. Chemically it is the glycerol ester of stearic acid.
Contents
- 1Structure, synthesis, and occurrence
- 2Uses
- 3See also
- 4Compendial status
- 5References
Structure, synthesis, and occurrence
Glycerol monostearate exists as three stereoisomers, the enantiomeric pair of 1-glycerol monostearate and 2-glycerol monostearate. Typically these are encountered as a mixture as many of their properties are similar.Commercial material used in foods is produced industrially by a glycerolysis reaction between triglycerides (from either vegetable or animal fats) and glycerol.[4]Glycerol monostearate occurs naturally in the body as a product of the breakdown of fats by pancreatic lipase. It is present at very low levels in certain seed oils.Uses
GMS is a food additive used as a thickening, emulsifying, anti-caking, and preservative agent; an emulsifying agent for oils, waxes, and solvents; a protective coating for hygroscopic powders; a solidifier and control release agent in pharmaceuticals; and a resin lubricant. It is also used in cosmetics and hair-care products.[5]GMS is largely used in baking preparations to add "body" to the food. It is somewhat responsible for giving ice cream and whipped cream their smooth texture. It is sometimes used as an antistaling agent in bread.See also
- Glyceryl hydroxy stearate
- Monolaurin
Compendial status
References
- ^ Averill, H. P.; Roche, J. N.; King, C. G. (March 1929). "SYNTHETIC GLYCERIDES. I. PREPARATION AND MELTING POINTS OF GLYCERIDES OF KNOWN CONSTITUTION". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 51 (3): 866–872. DOI:10.1021/ja01378a032.
- ^ Buchnea, Dmytro (February 1967). "Acyl migration in glycerides. I. A bimolecular resonant ion complex as an intermediate in acyl migration of monoglycerides". Chemistry and Physics of Lipids. 1 (2): 113–127. DOI:10.1016/0009-3084(67)90004-7.
- ^ Jens Birk Lauridsen (1976). "Food emulsifiers: Surface activity, edibility, manufacture, composition, and application". Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society. 53 (6): 400–407. DOI:10.1007/BF02605731.
- ^ Sonntag, Norman O. V. (1982). "Glycerolysis of fats and methyl esters — Status, review, and critique". Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society. 59 (10): 795A–802A. DOI:10.1007/BF02634442. ISSN 0003-021X.
- ^ Glycerol monostearate Cheminfo
- ^ The British Pharmacopoeia Secretariat (2009). "Index, BP 2009" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 April 2009. Retrieved 18 March 2010.
Glycerol monostearate  1-glycerol monostearate (1-isomer)
1-glycerol monostearate (1-isomer)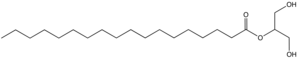 2-glycerol monostearate (2-isomer)
2-glycerol monostearate (2-isomer)Names IUPAC name 2,3-Dihydroxypropyl octadecanoicOther names Glyceryl monostearate
Glycerin monostearate
MonostearinIdentifiers - Compounds
- (Mix): Mixture of 1- and 2- isomers
- (1-): 1-glycerol monostearate
- (2-): 2-glycerol monostearate
- (Mix): 31566-31-1

- (1-): 123-94-4
- (2-): 621-61-4
3D model (JSmol)- (Mix): Interactive image
Abbreviations GMS ChEMBL - (Mix): ChEMBL255696

ChemSpider - (Mix): 23095

ECHA InfoCard 100.004.242 KEGG - (Mix): D01947

PubChem CIDCompTox Dashboard (EPA)- (Mix): DTXSID7029160

Properties C21H42O4 Molar mass 358.563 g·mol−1 Appearance White solid Density 1.03 g/cm3 Melting point (Mix) 57–65 °C (135–149 °F)
Insoluble Hazards Flash point 230 °C (446 °F) (open cup) Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). verify (what is
verify (what is 
 ?)
?)Infobox references FOR MORE INFORMATION POST ME A COMMENT



0 Response to "Glycerol monostearatehow to dissolve glycerol monostearate, glycerol monostearate banned, glycerol monostearate vegan, glycerol monostearate solubility, glycerol monostearate e471, glycerol monostearate safety, glycerol monostearate in cosmetics, glycerol monostearate halal"
Post a Comment